
Types of Outbound Orders in the Fulfillment Process
It’s important for businesses to have a comprehensive understanding of the different types of outbound orders. These orders are crucial parts of the supply chain and go through different stages of the fulfillment process. They vary based on product type, specific customer requirements, and destination. Here, we explore the different order types in the fulfillment process.
Dropshipping Orders
Drop shipping is a supply chain management method where the retailer does not keep the products it sells in stock. Instead, when a retailer sells a product, it purchases the item from a third party and has it shipped directly to the customer. This means that the retailer does not have to deal with the costs and complexities of storing and managing inventory.
3PL Orders (Third Party Logistics)
3PL is a model where items are stored and delivered by a third party. As we discussed before, retailers outsource their logistics operations to a 3PL provider, which handles the storage and shipping of supplies. 3PL providers oversee the movement and storage of goods within a warehouse. Warehouse management consists of supply management, order processing, and fulfillment.
For a more detailed explanation and comparison between the Dropshipping and 3PL models visit our blog 3PL VS Drop Shipping: What is the right model to scale your business operations
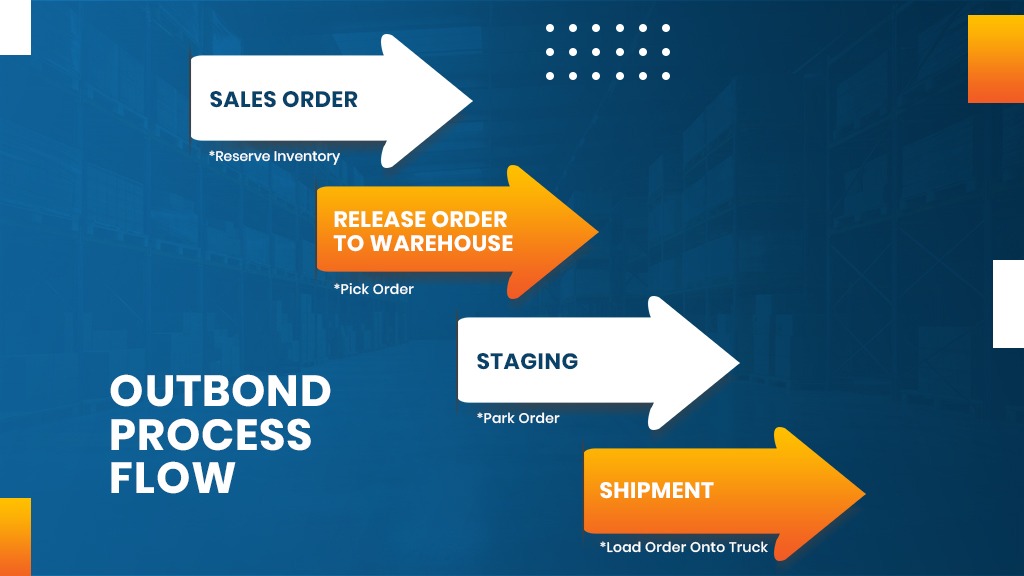
The image above shows the standard process flow for all orders; whatever form they are in, their broad processing features are almost the same.
B2C Orders (Business to Customer)
B2C orders are customer orders, the most common type of order in fulfillment. These are purchases made by individual consumers, whether physically in stores and markets or through online platforms such as AliExpress and Amazon.
- B2C order fulfillment requires a fulfillment system capable of quick order processing and delivery.
- E-commerce fulfillment is the process of receiving, processing, and delivering online orders to consumers.
- Picking and packing orders involves selecting items from the supply and packaging them based on consumer orders.
Subscription Orders
Subscription orders are recurring deliveries sent to consumers who have subscribed for daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, or half-yearly subscriptions. These consumers want a fixed shipment of certain products, be it newspapers, magazines, or cat litter.
Top Priority Orders
There are certain types of orders that are prioritized by fulfillment companies. This could include fast delivery of perishable items such as fruits, as any delay could cause the food to decay.
Another example is to carefully handle and package delicate and breakable items. If they arrive damaged to the customer, it could result in negative reviews and complaints. Most businesses also give priority to large-scale orders made by big companies as these have a greater profit margins, and fast delivery might lead to repeat business and revenue increase.
Wholesale Distributor Orders.
These are also called business-to-business (B2B) Orders. They are placed by companies and businesses that require goods for resale, large-scale production, or other purposes. These orders are usually large in volume and have specific packaging and delivery requirements. B2B order fulfillment requires an efficient fulfillment system for order processing, supply management, packaging, and delivery.
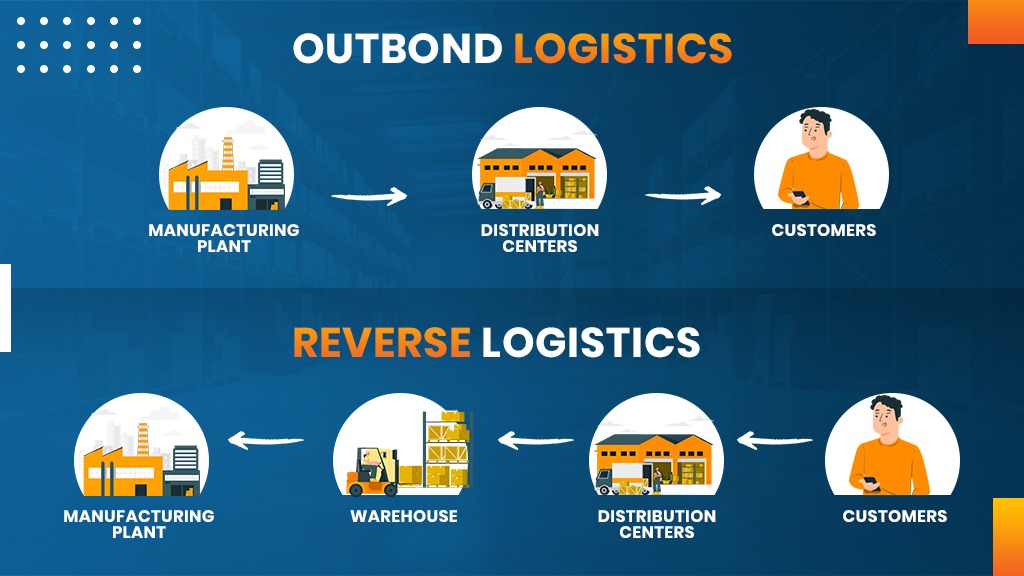
Reverse Logistics
Returns are an essential part of any efficient fulfillment management system. While returns are not outbound orders, handling returns, also known as reverse logistics, is crucial for any logistics system.
The reverse logistics process involves managing the return of products from consumers to the fulfillment center or manufacturer. Consumers typically return products due to defects, dissatisfaction, or other reasons. Therefore, having a robust system in place to handle returns is vital for overall customer satisfaction and the smooth operation of the supply chain.
International Orders
International orders involve transportation across national borders, which complicates the fulfillment process. Efficient order fulfillment of import/export orders requires coordination with international logistics companies and adherence to international transport regulations.
Export orders require adherence to the import laws of the destination country. Import orders require bringing products from global suppliers to the home country.
Conclusion
It’s important for businesses to have a comprehensive understanding of the different types of outbound orders in fulfillment. This includes orders from individual customers, retail stores, wholesalers, distributors, and other businesses.
By gaining insight into these various order types, companies can effectively optimize their logistics operations to efficiently handle different order volumes and requirements. This strategic approach allows businesses to stay ahead in a competitive economy and meet the diverse needs of their customers and partners.




Leave a Reply